Object Oriented JavaScript
Object-oriented programming is used to representations of objects in the real world. It usually bundles up related dates and functions in one object. The problem is how we can put it together? In this post, I talk about three ways of Creating objects Object.create function class and prototype.
Object.create
What is a prototype?
The prototype is about relationships between two objects that allow an object to access another object's property. if many object have a same property, we can put this property to another object and link those object
let user1 = { name: 'EVA', level: 2 }
let user2 = { name: 'Bule', level: 0 }
let base = { levelUp() { level = this.level + 1 } }
Object.setPrototypeOf(user1, base)
Object.setPrototypeOf(user2, base)
user1.levelup()Object.setPrototypeOf(user1, base) link user1 to base. JavaSript looks for the property directly on user1, but can't find it. Then looks at base object. user1 can access property on base, we say base is a prototype* of user1 and user1 is inherit from base. if many object link togther it become prototype chain**.
Note: for details of how JavaSript access and set value, please check the book YDKJS [[Put]] and [[Get]] section.
Object.create
Object.create returns out an empty object, setting an existing object as the prototype of the newly created object. user1 is a empty object that linked to base object, them we add property to it
let base = { levelUp() { level = this.level + 1 } }
let user1 = Object.create(base)
user1.name = 'EVA'
user1.level = 2
user1.levelup()New & this
The new keyword
what does new do?
newcreate new empty object.- hidden proto property link to constructor's prototype property
- return object
function CreateUser(name) {
this.name = name
this.level = 1
}
CreateUser.prototype.levelUp() = function levelUp() { level = this.level + 1 }
let user1 = new Foo('EVA')new create an object, then CreateUser set property to new created object, next link object to CreateUser.prototype. (ignore constructor property here). This process is similar to manual creating. let compare them:
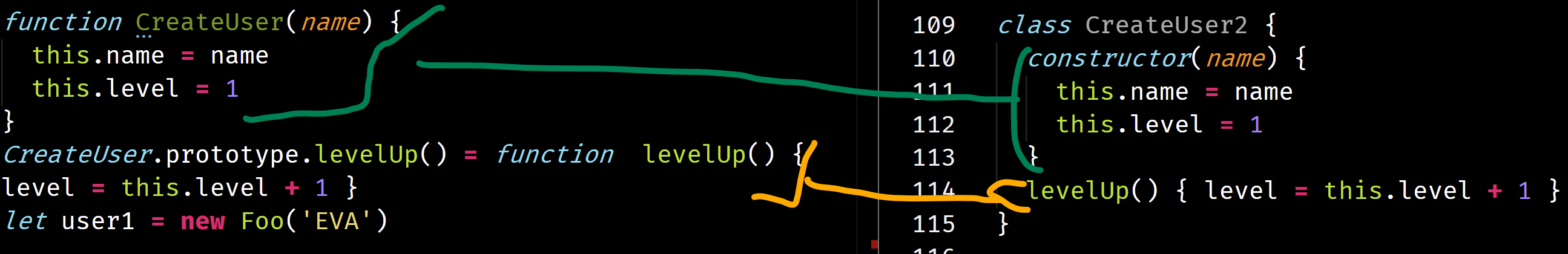
CreateUser.prototype is an object, so that we can replace it with our own object { .. }. others are straightforward.
This keyword
this is some rule for find value. they are
| Invocation form | this |
|---|---|
| function | global object / undefined |
| method | the object |
| constructor | the new object |
| apply | argument |
| array function | this in ourer scope |
following this rule is easy to figure out this value. you can find some examples in internet.
Class
Class in javascript is a syntactical sugar. We’re writing our prototype methods separately from our object ‘constructor’ itself. class let us put in same block.
class CreateUser2 {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name
this.level = 1
}
levelUp() { level = this.level + 1 }
}let's compare class with function:

Wapping up
In Javascript, we have many ways to create object: function Constructor, Object.create, Classes. using class and function to create an object is usually complicated and confusing. the base way is Object.create